Understanding Tendonitis and Osteoporosis
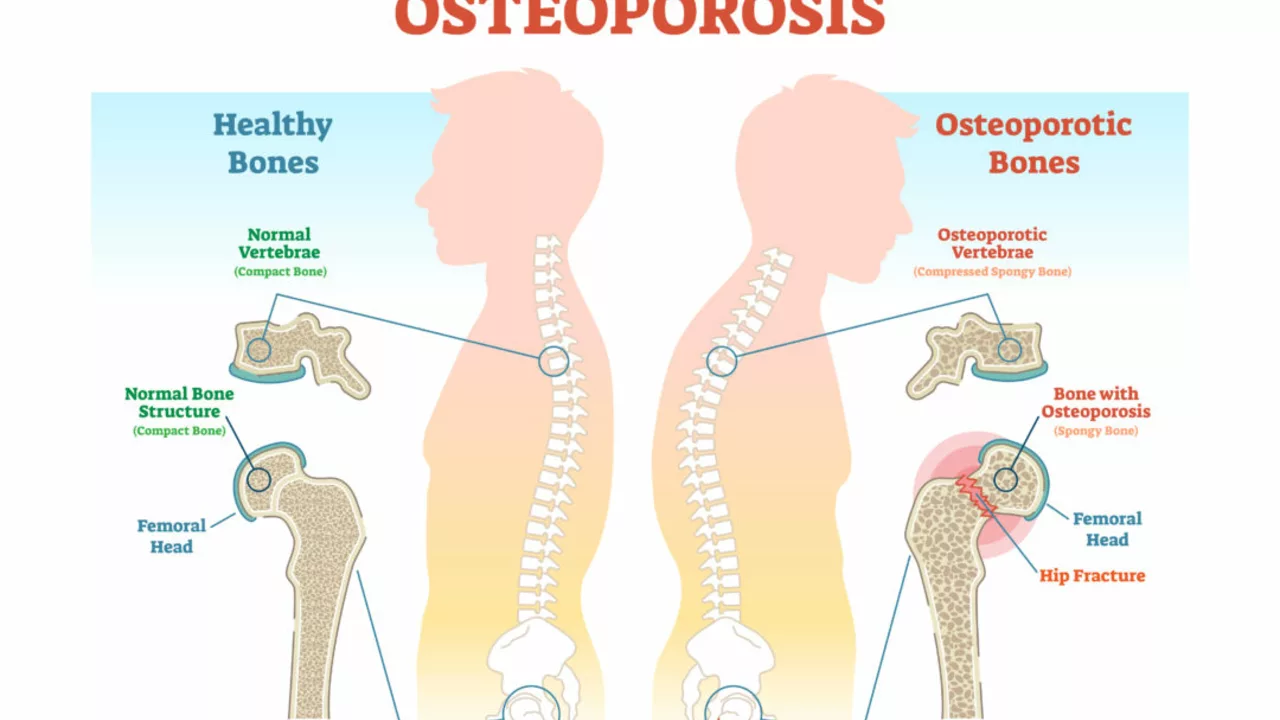
As a health blogger, I've spent significant time researching and understanding various health conditions, including tendonitis and osteoporosis. Although these two conditions might appear unrelated at first glance, there is a fascinating connection between them. Tendonitis refers to the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone. On the other hand, osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone or makes too little bone, causing the bones to become weak and brittle.
The Underlying Causes of Tendonitis and Osteoporosis
When it comes to tendonitis, the primary cause is often overuse or injury of a specific tendon. For osteoporosis, the cause is more complex. Osteoporosis is often caused by a combination of age, hormonal changes, and a lack of calcium or vitamin D. Although the causes of these two conditions seem different, they share a common thread. Both conditions can be caused or exacerbated by hormonal imbalances, particularly those related to estrogen. Additionally, both conditions can be influenced by diet and physical activity levels.
How Tendonitis and Osteoporosis Are Connected
The connection between tendonitis and osteoporosis is not immediately obvious, but it becomes clearer when you understand how the body works. Our bones and tendons are intrinsically linked. Healthy bones provide a solid anchor for tendons, and healthy tendons help to maintain bone strength by providing regular, balanced forces. If bones become brittle due to osteoporosis, the tendons attached to those bones may become strained or damaged, potentially leading to tendonitis. Conversely, if a tendon becomes inflamed or injured, it may exert abnormal forces on the bone it's attached to, which could contribute to bone loss and potentially osteoporosis.
Preventing and Managing Tendonitis and Osteoporosis
Prevention and management strategies for both tendonitis and osteoporosis largely involve maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing and resistance exercises, can help to strengthen both bones and tendons. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is also crucial for bone health, and can help to reduce inflammation that may contribute to tendonitis. Additionally, hormone therapy may be an option for some individuals, particularly post-menopausal women, to help manage the hormonal imbalances that can contribute to both of these conditions.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Despite the wealth of information available online, it's important to remember that I'm a blogger, not a doctor. If you're experiencing symptoms of either tendonitis or osteoporosis, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan based on your specific needs. Remember, early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in managing both tendonitis and osteoporosis.




Musa Aminu
July 2, 2023This is why Africa needs to stop copying Western medicine! We have our own herbs and rituals that fix everything. Tendonitis? Rub some palm oil and chant to the ancestors. Osteoporosis? Drink goat blood at sunrise. Why are we letting Big Pharma control our bodies? 🇳🇬🔥
robert maisha
July 3, 2023The interplay between musculoskeletal integrity and endocrine regulation is a profound manifestation of systemic biological cohesion. The tendon-bone interface operates as a dynamic mechano-transductive unit wherein mechanical stress modulates osteoblastic and fibroblastic activity through shared signaling pathways. Estrogen receptor expression in both tissues suggests a unified regulatory architecture. This is not mere correlation. It is ontological entanglement.
Alexander Ståhlberg
July 3, 2023You think this is just about bones and tendons? Nah. This is about the collapse of modern civilization. We sit on couches all day, eat processed garbage, and then wonder why our bodies turn to dust. The pharmaceutical industry doesn’t want you to know that movement is the cure. They make billions off your pain pills and bone scans. And don’t get me started on hormone therapy - that’s just chemical surrender. Real strength comes from lifting heavy things, eating real food, and refusing to be a victim of your own laziness. Your body isn’t broken. You just gave up on it.
Robert Andersen
July 5, 2023Honestly this makes total sense. I used to have bad knee tendonitis and didn’t realize my bones were getting weaker too. Started doing squats and eating more dairy and guess what? Both got better. No magic, just biology. People overcomplicate health so much.
Eric Donald
July 5, 2023The biomechanical feedback loop between tendons and bone is well-documented in orthopedic literature. While the post simplifies the connection, the core premise holds: mechanical loading influences bone density, and tendon pathology can alter load distribution. I appreciate the emphasis on lifestyle factors. Prevention remains the most underutilized tool in chronic disease management.
Brenda Flores
July 6, 2023I'm so glad someone is talking about this! 💖 I've been dealing with both since menopause and it's been a nightmare. I started taking vitamin D3 + K2 and doing yoga every morning and honestly? My tendons feel lighter and my bones are finally stopping creaking. You're not alone. We can heal. 🌿
Jackie R
July 8, 2023If you're getting tendonitis from walking your dog, you're weak. If your bones are crumbling, you're lazy. Stop blaming hormones. Go lift something. Or don't. But don't act like it's a mystery.
Josh Arce
July 9, 2023Tendonitis? That's just inflammation. Osteoporosis? That's bone decay. They're not connected. You're just trying to sound smart. The real cause? Too much sitting. And too much soy milk.
Eli Grinvald
July 10, 2023This is actually really helpful 😊 I didn't realize my wrist pain could be linked to my bone density. I'm gonna start walking more and eating almonds. Thanks for putting this out there!
Alexis Hernandez
July 12, 2023Man, I used to think tendons were just ropes holding muscles to bones. Turns out they're like little shock absorbers that also whisper to your skeleton. It's wild how the body talks to itself. I started doing farmer's carries and my knees stopped screaming. Also, I eat eggs now. Who knew?
brajagopal debbarma
July 13, 2023Oh wow. So you're saying if you don't exercise, your body falls apart? Groundbreaking. Next you'll tell me breathing is good for lungs.
Carly Smith
July 15, 2023I read this and I'm just like why do people even write this? Like just go to the gym. Or take a pill. Or whatever. I don't care. My hip hurts. End of story.
Kurt Stallings
July 15, 2023The body is a machine. Machines wear out. You're not special. Stop romanticizing tendons.
Angie Creed
July 16, 2023This is exactly what I've been saying since 2018. The patriarchy weaponizes estrogen deficiency to keep women docile. They sell you calcium supplements while the real solution is radical self-love and rejecting capitalist health norms. I healed mine with crystal baths and fasting. You're welcome.
Michael Ferguson
July 17, 2023You think this is bad? Try living with both conditions after your husband left you, your kid went to college, and your job cut your hours. I’ve been taking 10,000 IU of vitamin D, doing resistance bands at 5am, and crying in the shower every day. No one talks about the emotional toll. The pain is physical, yes - but the loneliness? That’s what really fractures you. I’ve lost sleep, friendships, and my sense of worth. And you’re writing a blog post like it’s a TED Talk. I’m not a case study. I’m exhausted.
Patrick Klepek
July 19, 2023Funny how the post mentions estrogen but ignores testosterone’s role in tendon resilience. Also, did you know that in some cultures, tendonitis is treated with ice baths and fermented fish paste? Maybe the answer isn’t just calcium and yoga. Just saying.