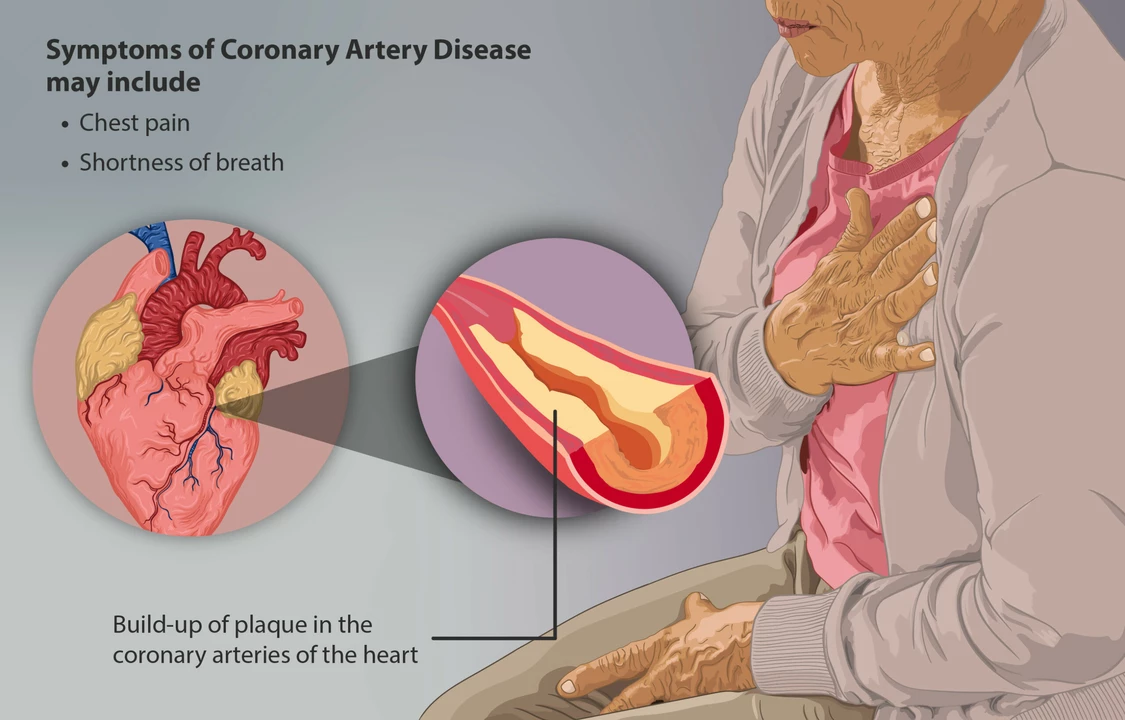
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease
Before diving into the benefits of exercise in managing and preventing coronary artery disease, it's important to first understand what this condition is. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a type of heart disease that occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, and even a heart attack if not treated properly. Fortunately, there are many ways to both manage and prevent CAD, and one of the most effective methods is through regular exercise. In this article, we'll explore the various benefits of exercise in managing and preventing this serious heart condition.
Improving Cardiovascular Fitness
One of the main benefits of exercise for managing and preventing coronary artery disease is its ability to improve cardiovascular fitness. Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, making it more efficient at pumping blood throughout the body. This can help lower blood pressure, reduce heart rate, and improve overall circulation, all of which are essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. In turn, this can significantly reduce the risk of developing CAD and help manage symptoms in those who already have the condition.
Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a key contributor to the development of CAD, as it can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries. Exercise has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body, helping to reduce the risk of plaque buildup and subsequent narrowing of the arteries. By engaging in regular physical activity, you can help to lower your body's inflammatory response, which can in turn help protect against coronary artery disease.
Managing Weight and Reducing Obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for coronary artery disease, as excess weight can put added strain on the heart and contribute to the development of other risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes. Exercise is a crucial component of any weight management plan, helping to burn calories and maintain a healthy body weight. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, you can help to prevent obesity and its associated risks, including CAD.
Lowering Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels are another major risk factor for the development of coronary artery disease. Exercise has been shown to help lower both total cholesterol and LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels while increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol. This can help to prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries and reduce the risk of CAD. By engaging in regular physical activity, you can help to manage your cholesterol levels and protect your heart health.
Reducing Stress and Improving Mental Health
Stress and poor mental health can both contribute to the development of coronary artery disease, as they can lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices and increased inflammation in the body. Exercise is a natural stress reliever, helping to release endorphins and improve mood. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can help to reduce stress, improve mental health, and decrease your risk of CAD.
Enhancing Blood Sugar Control
Diabetes and high blood sugar levels are major risk factors for coronary artery disease, as they can damage blood vessels and contribute to the formation of plaque. Exercise helps to improve blood sugar control by increasing insulin sensitivity and promoting the uptake of glucose by the body's cells. By engaging in regular physical activity, you can help to manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of developing CAD.
Improving Sleep Quality
Poor sleep quality is another factor that can contribute to the development of coronary artery disease, as it can lead to increased stress, inflammation, and other health problems. Exercise has been shown to improve sleep quality by helping to regulate the body's natural sleep-wake cycle and promoting deeper, more restful sleep. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine, you can help to improve your sleep quality and reduce your risk of CAD.
Creating a Healthy Exercise Routine
Now that we've explored the many benefits of exercise in managing and preventing coronary artery disease, it's important to create a healthy exercise routine that works for you. This can include a combination of aerobic activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, as well as strength training and flexibility exercises. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week, along with two days of strength training. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise program, especially if you have existing health conditions or concerns.




Alexis Hernandez
May 15, 2023I never thought about how exercise literally reprograms your body to fight heart disease. It's not just about losing weight or getting buff-it's like your heart becomes a better, smarter pump. I started walking 30 mins a day after my dad's scare, and now I sleep like a baby, my blood pressure's down, and I don't feel like a zombie by 3 PM. Seriously, if you're sitting there thinking 'I don't have time,' you just need to start with 10 minutes. Your future self will high-five you.
brajagopal debbarma
May 15, 2023Exercise? Really? Next you'll tell me sunlight cures cancer. My grandpa worked 60 hours a week lifting bricks his whole life and died of a heart attack at 58. Funny how the 'experts' always ignore the outliers.
Carly Smith
May 15, 2023So you're saying if I just run around yelling at my cat I'll live longer? Lol. I tried yoga once. I cried. The instructor cried. The dog left the room. I'm not doing it again
Angie Creed
May 16, 2023You're all missing the point. Exercise doesn't prevent disease-it just delays the inevitable. We're all going to die. The real question is: do you want to die with a treadmill in your garage or a morphine drip in your IV? The system wants you to believe movement = health. But what if the real problem is capitalism? What if the real cure is quitting? I'm not buying it.
Michael Ferguson
May 17, 2023I've read every single study on this. I've got 17 PDFs saved on my desktop titled 'CAD and Exercise - FINAL'. And let me tell you, the data is overwhelming. People who exercise live 7.2 years longer on average. But here's what nobody tells you-most of those people are also rich, white, and have personal trainers. The rest of us are working two jobs and eating gas station burritos. So yeah, 'just exercise' is the most privileged advice in history. I've been told to 'just walk more' while my kid's in the ER because the insulin ran out. So don't preach. Just... don't.
Caden Little
May 19, 2023Hey everyone, I'm a cardiac rehab nurse and I see this every day. One of my patients, 72, started with just standing up from his chair 5 times a day. Now he walks 2 miles and dances with his wife on weekends. It’s not about intensity-it’s about showing up. Even a 5-minute stretch counts. You don’t need a gym. Just move. I promise your heart will thank you. 💪❤️
Sebastian Brice
May 19, 2023I used to think 'exercise' meant sweating buckets in a gym. Then I started dancing in my kitchen to 90s hip-hop. No one saw me. I didn’t care. I felt lighter. Like my chest wasn’t full of wet concrete anymore. I still don't 'work out.' But I move. And honestly? That’s the secret. You don’t have to be perfect. Just be present.
Jim Aondongu
May 20, 2023In Nigeria we dont have gyms but we walk everywhere. Our grandmas climb hills with 50kg on their head. We dont need science to tell us movement is good. We live it. But you westerners think exercise is a trend like keto or yoga pants. Its just life
Michael Schaller
May 22, 2023I had a heart scare last year. My doctor said 'walk more.' I thought he was joking. But I started walking to the mailbox. Then to the corner store. Then around the block. Now I walk 5 miles every morning before work. I don't feel like I'm 'getting fit.' I feel like I'm getting back my life. And that’s worth more than any stat.
Kyle Tampier
May 23, 2023They’re hiding the truth. Exercise is a distraction. The real cause? Fluoride in the water. And the pharmaceutical industry. They make billions off heart meds. You think they want you to heal? They want you to keep buying pills. Walk? Sure. But ask WHO funds the 'exercise is medicine' campaigns.
Tom Caruana
May 24, 2023I tried to start exercising but my knees hurt and my dog licked my sweat and now I think I'm allergic to motivation?? 😭 I just want to nap. And eat tacos. And maybe watch Netflix. But my heart feels heavy. Help? 🤕❤️
Muzzafar Magray
May 25, 2023Everyone talks about exercise like it's magic. But what about the people who can't move? The disabled? The chronically ill? You act like everyone has the same body, same time, same privilege. Your 'just move' advice is just another form of ableism wrapped in a yoga mat.
Alexis Hernandez
May 26, 2023To the person who said 'just move' is ableist-I hear you. And I’m sorry. My comment was tone-deaf. What I meant is: movement doesn’t have to look like running or lifting. It can be breathing deeply. Stretching in bed. Rolling your shoulders. Even standing up to change a TV channel counts if you’re stuck. The goal isn’t perfection. It’s presence. Thanks for calling it out.